- Introduction
- Facts about Zimbabwe History
- Facts about Zimbabwe Culture
- Facts about Zimbabwe Geography
- Facts about Zimbabwe Political Situation
- Facts about Zimbabwe Economy
- Facts about Zimbabwe Society
- Facts about Zimbabwe Ethnic Diversity
- Facts about Zimbabwe Languages
- Facts about Zimbabwe Religion
- Facts about Zimbabwe Conflict and War
- Facts about Zimbabwe Reconstruction Efforts
- Facts about Zimbabwe International Relations
- Humanitarian Issues
- Facts about Zimbabwe Women’s Rights
- Facts about Zimbabwe Education
- Facts about Zimbabwe Infrastructure
- Facts about Zimbabwe Natural Resources
- Facts about Zimbabwe Tourism
- Facts about Zimbabwe Future Prospects
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions & Answers
Introduction
Zimbabwe, a country known for its wealth in nature, culture, and beauty, has experienced significant changes since gaining independence in 1980. From its colonial past as Southern Rhodesia to economic and political struggles, Zimbabwe’s history is marked by resilience and growth. This article explores various facts about Zimbabwe, including its rich history, diverse culture, geographic features, political landscape, economy, society, ethnic diversity, languages, religion, conflicts, and future prospects. From Victoria Falls to Great Zimbabwe ruins, this landlocked country holds treasures in its landscapes and people.
Facts about Zimbabwe History
- Zimbabwe was previously known as Southern Rhodesia, named after Cecil Rhodes, an English money manager and colonizer.
- In 1965, the white minority government under Ian Smith pronounced freedom from England, prompting a significant stretch of worldwide detachment.
- The nation acquired autonomy from English provincial rule in 1980, with Robert Mugabe turning into its most memorable state leader.
- Mugabe’s standard, at first hailed for compromise endeavors, later became set apart by dictatorship, monetary botch, and denials of basic liberties.
- Land change arrangements in the mid-2000s brought about the questionable capture of white-claimed ranches, causing monetary unrest.
- Hyperinflation in 2008 prompted the deserting of the Zimbabwean dollar, with the nation taking on a multi-cash framework.
- The solidarity government framed in 2009 between Mugabe’s ZANU-PF and the resistance settled the economy somewhat.
- Mugabe was expelled from power in 2017, finishing his 37-year rule, and Emmerson Mnangagwa took over as president.
- The nation keeps on wrestling with difficulties like joblessness, defilement, and political constraint.
- Recent years have seen endeavors to draw in unfamiliar speculation and work on global relations for monetary recuperation.
Facts about Zimbabwe Culture
- Zimbabwe has a rich social legacy, with different impacts from Shona, Ndebele, and other ethnic gatherings.
- Traditional music and dance, for example, the mbira (thumb piano) and the fiery “Gwara,” are basic pieces of Zimbabwean culture.
- The nation is popular for its stone models, with craftsmen like Dominic Benhura acquiring worldwide approval.
- Shona figure, known for its profound subjects and utilization of neighborhood materials like serpentine stone, is a noticeable fine art.
- The writing scene flaunts journalists like Chenjerai Hove and Tsitsi Dangarembga, whose works frequently reflect Zimbabwean life and history.
- Traditional functions like the Bira, which praises hereditary spirits, are as yet rehearsed in numerous networks.
- Cricket is a well-known sport in Zimbabwe, with the public group taking part in global rivalries.
- The dynamic texture known as “Chitenge” or “Shweshwe” is much of the time worn as conventional clothing.
- Cuisine incorporates dishes like sadza (maize feast), nyama (meat) stew, and muriwo (salad greens).
- The Extraordinary Zimbabwe ruins, an UNESCO World Legacy Site, are an image of the country’s verifiable riches and culture.
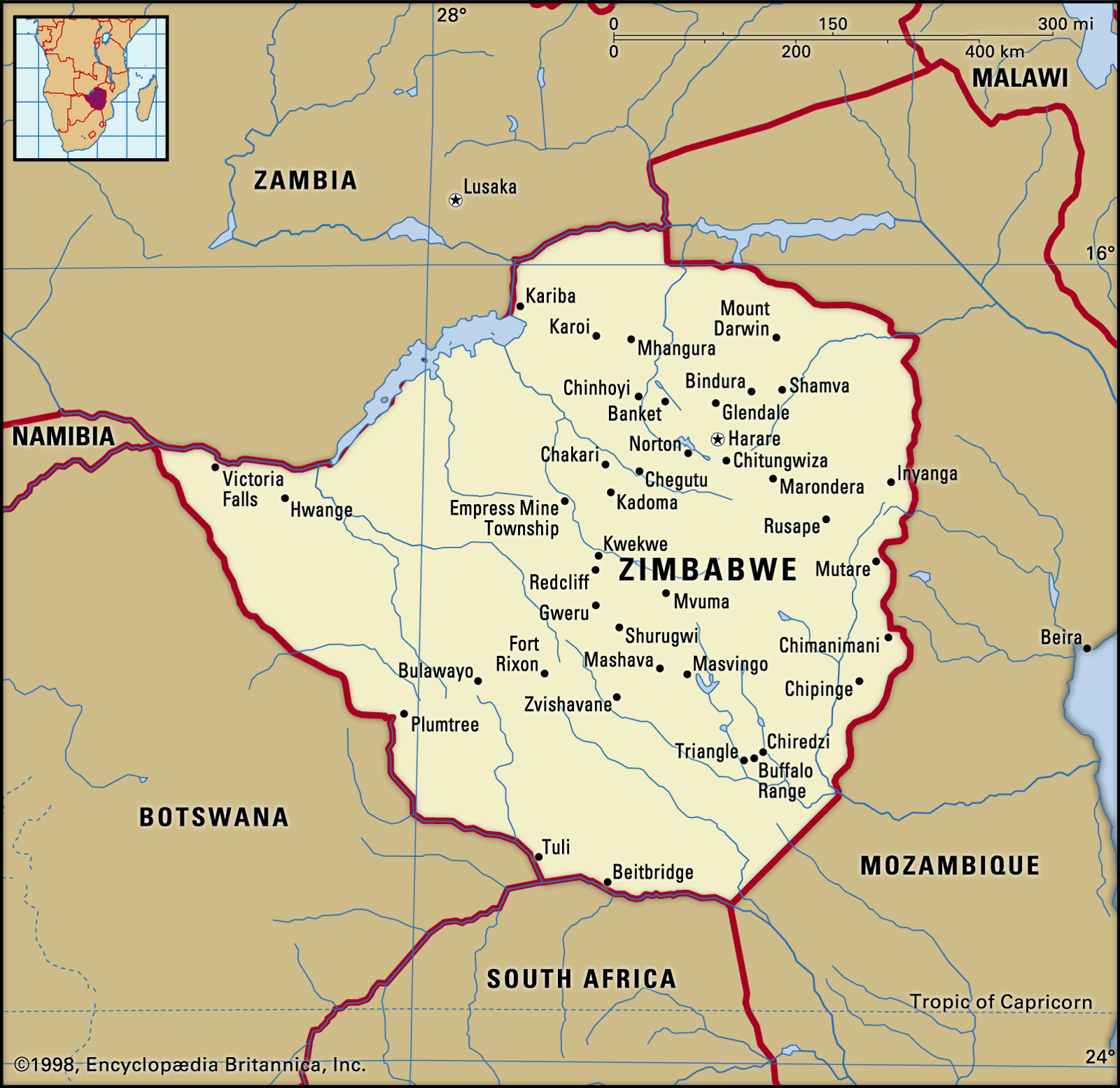
Facts about Zimbabwe Geography
- Zimbabwe is a landlocked nation situated in southern Africa, lined by Zambia, Mozambique, South Africa, and Botswana.
- The scene goes from highveld (level) to mountains, with the Eastern Good countries giving a beautiful background.
- The Zambezi Waterway shapes the northern boundary and is home to the noteworthy Victoria Falls, a significant vacation spot.
- Hwange Public Park is perhaps of Africa’s biggest game save, well known for its different untamed life including elephants, lions, and giraffes.
- Lake Kariba, made by the damming of the Zambezi Waterway, is one of the world’s biggest man-made lakes and offers fishing and drifting.
- The Matobo Slopes, known for their exceptional stone developments and antiquated San rock workmanship, hold social and verifiable importance.
- Zimbabwe encounters a subtropical environment with unmistakable wet and dry seasons.
- Agriculture is an imperative area, with prolific soils in certain districts supporting yields like maize, tobacco, and cotton.
- Mining is huge, with Zimbabwe known for its stores of platinum, gold, and precious stones.
- The nation faces natural difficulties like deforestation and soil corruption.
Facts about Zimbabwe Political Situation
- Zimbabwe works under a semi-official framework, with the president as the head of state and government.
- The decision party, ZANU-PF, has been in power since autonomy in 1980, in spite of the fact that confronting expanding resistance lately.
- Emmerson Mnangagwa, a previous partner of Robert Mugabe, has been president since Mugabe’s removing in 2017.
- Elections in Zimbabwe have frequently been damaged by claims of anomalies and brutality.
- Opposition gatherings like the Development for Popularity based Change (MDC) have confronted concealment and captures.
- Mnangagwa’s administration has been centered around financial change and drawing in unfamiliar venture.
- The government has put forth attempts to further develop relations with Western nations, looking to rejoin the District.
- There are continuous discussions about the requirement for protected changes to reinforce majority rule foundations.
- Human privileges associations keep on scrutinizing the public authority for crackdowns on contradiction and the right to speak freely of discourse.
- The political circumstance stays complex, with difficulties of debasement, joblessness, and neediness impacting soundness.
Facts about Zimbabwe Economy
- Zimbabwe’s economy has battled with out of control inflation and financial downfall, especially during the 2000s.
- The nation encountered a pinnacle out of control inflation pace of 89.7 sextillion percent in 2008, prompting the relinquishment of the Zimbabwean dollar.
- Agriculture, mining (especially gold, platinum, and precious stones), and the travel industry are key areas.
- Land change approaches in the mid-2000s, pointed toward reallocating land from white ranchers to dark Zimbabweans, caused disturbances in horticultural creation.
- The multi-money framework, including the utilization of the US dollar and South African rand, settled the economy somewhat.
- Informal area exercises, for example, road distributing and distinctive mining, assume a huge part in the economy.
- The government has carried out starkness gauges and looked for global credits to settle the economy.
- Infrastructure, including streets and energy supply, requires critical speculation and improvement.
- Unemployment and underemployment rates stay high, especially among youth.
- Economic development possibilities are attached to political strength, speculation environment, and worldwide ware costs.
Facts about Zimbabwe Society
- Zimbabwe has a populace of different ethnic gatherings, with the Shona and Ndebele being the biggest.
- Family and local area are fundamental to Zimbabwean culture, with more distant families frequently living respectively and supporting one another.
- Traditional upsides of regard for seniors and communalism are profoundly instilled.
- Urbanization has expanded, with Harare being the biggest city and financial center point.
- Education is profoundly esteemed, despite the fact that admittance to quality training can be restricted in provincial regions.
- Healthcare difficulties incorporate restricted assets, mind channel of clinical experts, and HIV/Helps predominance.
- The nation has a generally youthful populace, with a middle period of something like 20 years.
- Traditional healers, known as “n’anga” or “sangoma,” are as yet counseled close by current medical care.
- Gender jobs can be conventional, however there are continuous endeavors to advance orientation equity.
- Social issues like neediness, wrongdoing (especially in metropolitan regions), and substance misuse are difficulties.
Facts about Zimbabwe Ethnic Diversity
- The Shona individuals are the biggest ethnic gathering in Zimbabwe, making up around 70% of the populace.
- The Ndebele individuals, relatives of the Zulu who moved from South Africa, comprise around 20% of the populace.
- Other ethnic gatherings incorporate the Tonga, Chewa, Kalanga, Venda, Sotho, and various more modest gatherings.
- Each ethnic gathering has its own language, customs, and customs.
- The Shona are additionally partitioned into sub-bunches like the Zezuru, Karanga, Manyika, and Ndau.
- The Ndebele are known for their dynamic workmanship, beadwork, and particular estates.
- Ethnic variety is praised in Zimbabwean culture through music, dance, and celebrations.
- Despite variety, pressures have once in a while emerged, particularly during times of political unsteadiness.
- Traditional authority among various ethnic gatherings assumes a part in neighborhood administration.
- Zimbabwe’s constitution perceives and advances the privileges of every single ethnic gathering.
Facts about Zimbabwe Languages
- Zimbabwe perceives 16 authority dialects, mirroring its different ethnic sythesis.
- English is the fundamental language utilized in government, business, and training.
- Shona is the most broadly communicated in native language, with varieties like Zezuru, Karanga, Manyika, and Ndau.
- Ndebele is the second most communicated in native language, basically among the Ndebele public.
- Other native dialects incorporate Chewa, Chibarwe, Kalanga, Koisan, Nambya, Ndau, Shangani, Sotho, Tonga, Tswana, Venda, and Xhosa.
- The utilization of native dialects is elevated in schools to safeguard social legacy.
- Many Zimbabweans are multilingual, communicating in English and somewhere around one native language.
- Radio stations and papers are accessible in different native dialects to take special care of various networks.
- Language can be a wellspring of social pride and character, particularly among more youthful ages.
- Efforts are continuous to normalize and advance the utilization of native dialects in schooling and media.
Facts about Zimbabwe Religion
- Zimbabwe is strictly assorted, with Christianity being the prevailing religion.
- Protestantism, including different sections like Anglicanism, Methodism, and Pentecostalism, is boundless.
- Roman Catholicism has a huge following, especially among the Ndebele people group.
- Traditional African religions are drilled close by Christianity, consolidating convictions in genealogical spirits and customary ceremonies.
- Islam is a minority religion, primarily among the Indian and Mozambican people group.
- Religious rehearses frequently cross with social customs, particularly in services and transitional experiences.
- Churches assume a conspicuous part in friendly administrations, training, and local area improvement.
- Religious get-togethers, for example, faith gatherings and celebrations, are significant occasions in many Zimbabweans’ lives.
- Religious pioneers now and then assume persuasive parts openly talk and governmental issues.
- Freedom of religion is ensured in the constitution, and strict resilience is by and large noticed.
Facts about Zimbabwe Conflict and War
- Zimbabwe has a complicated history of contention, from pioneer battles to nationwide conflicts.
- The First Chimurenga (1896-1897) was a disobedience to English rule by the Shona and Ndebele people groups.
- The Second Chimurenga, otherwise called the Rhodesian Shrubbery War (1964-1979), was a guerrilla battle against white minority rule.
- The conflict prompted Zimbabwe’s autonomy in 1980 yet additionally left profound scars on the country.
- Gukurahundi (1983-1987) alludes to a progression of slaughters did by the public authority against the Ndebele public.
- Land change in the mid-2000s ignited struggle between white ranchers and the public authority, prompting brutality and financial disturbance.
- Political viciousness around races, especially in 2008, brought about passings and relocation.
- Despite the finish of the nationwide conflict period, political pressures and incidental brutality continue.
- Issues of ethnic segregation and underestimation have been wellsprings of contention.
- Efforts at public mending and compromise have been made, including the foundation of the Public Harmony and Compromise Commission.
Facts about Zimbabwe Reconstruction Efforts
- Zimbabwe has embraced different remaking endeavors to address past difficulties and advance turn of events.
- Post-autonomy, endeavors were centered around schooling, medical care, and framework advancement.
- Land change arrangements during the 2000s planned to rearrange land from white ranchers to dark Zimbabweans, albeit the interaction was disputable.
- The government has looked for global help and advances for monetary recuperation and framework projects.
- Initiatives like the Momentary Adjustment Program (TSP) have planned to balance out the economy and draw in speculation.
- The World Bank and other global associations have offered help for social administrations and destitution decrease.
- Reconstruction endeavors have included reconstructing organizations, like the legal executive and public administrations.
- Infrastructure tasks, like street development and energy age, have been focused on for financial development.
- Land change stays a critical part of remaking, holding back nothing conveyance.
- Challenges, for example, defilement and political unsteadiness have now and again ruined these endeavors.
Facts about Zimbabwe International Relations
- Zimbabwe has had complex global relations, formed by its set of experiences of imperialism and post-freedom approaches.
- Relations with Western nations, especially the UK and the US, have been endured times because of common liberties concerns.
- The government has looked for nearer attaches with China, Russia, and other non-Western nations for speculation and backing.
- Membership in territorial associations like the African Association (AU) and Southern African Advancement People group (SADC) is critical for strategy.
- Zimbabwe’s part in territorial peacekeeping endeavors, for example, in the Vote based Republic of Congo, has been perceived.
- The nation has been associated with worldwide economic alliance, expecting to help its economy.
- Diplomatic endeavors have zeroed in on reconnecting with the global local area, including looking for readmission to the Republic.
- Zimbabwe has facilitated global meetings and occasions, displaying its true capacity for the travel industry and speculation.
- Relations with adjoining nations like South Africa and Zambia are significant for exchange and territorial security.
- International assents forced on Zimbabwe in the past have affected its international strategy choices.
Humanitarian Issues
- Zimbabwe has confronted compassionate difficulties, including food uncertainty and catastrophic events.
- Droughts, especially in country regions, have prompted crop disappointments and food deficiencies.
- The 2019 Twister Idai caused inescapable pulverization, influencing countless individuals.
- Poverty rates stay high, with numerous Zimbabweans living underneath the destitution line.
- Healthcare foundation and administrations are stressed, particularly in provincial regions.
- HIV/Helps pervasiveness is a critical wellbeing concern, despite the fact that headway has been made in treatment and counteraction.
- Access to clean water and sterilization is a test in certain networks.
- Humanitarian associations like the Unified Countries offices and NGOs give help with regions, for example, food help and medical care.
- The government has teamed up with worldwide accomplices to address helpful necessities.
- Efforts to further develop versatility to catastrophic events and environmental change influences are continuous.
Facts about Zimbabwe Women’s Rights
- Women’s freedoms in Zimbabwe have seen upgrades yet keep on confronting difficulties.
- The constitution ensures orientation uniformity, yet customary and social standards can restrict ladies’ chances.
- Women are underrepresented in governmental issues and positions of authority, however endeavors have been made to increment portrayal.
- Gender-based brutality, including abusive behavior at home and youngster marriage, stays a huge issue.
- Initiatives like the Abusive behavior at home Demonstration and the Orientation Commission expect to address these difficulties.
- Women’s admittance to training has improved, prompting higher education rates among ladies.
- Economic strengthening programs for ladies business visionaries and ranchers have been executed.
- Maternal death rates have declined, halfway because of further developed medical care access.
- Women’s associations and common society assume dynamic parts in upholding for ladies’ freedoms.
- Cultural movements and instruction crusades are progressing to advance orientation correspondence and ladies’ strengthening.
Facts about Zimbabwe Education
- Education in Zimbabwe is exceptionally esteemed, with free essential and auxiliary training given by the public authority.
- The school system follows a 7-4-2 construction: seven years of essential, four years of optional, and two years of cutting edge level.
- There are public, private, and mission schools, with the last option frequently giving reasonable training in provincial regions.
- Zimbabwe has a high proficiency rate, one of the greatest in Africa.
- Universities, for example, the College of Zimbabwe and Midlands State College are very much respected.
- Challenges incorporate deficient subsidizing, educator deficiencies, and obsolete framework.
- The cerebrum channel of gifted experts, including educators, has impacted the nature of instruction.
- Vocational preparation and specialized schooling programs plan to give pragmatic abilities.
- Education has been impacted by monetary difficulties, like high expansion and restricted assets.
- The government has stressed science, innovation, designing, and arithmetic (STEM) training to satisfy present day labor force needs.
Facts about Zimbabwe Infrastructure
- Zimbabwe’s foundation incorporates streets, rail routes, air terminals, and energy organizations.
- The street network is broad, associating significant urban communities and country regions.
- The railroad framework, oversaw by the Public Rail lines of Zimbabwe, joins key financial focuses.
- Airports, for example, Harare Global Air terminal and Victoria Falls Worldwide Air terminal serve homegrown and worldwide flights.
- Energy age depends on a blend of hydroelectric, warm, and sun-based power.
- Power blackouts, nonetheless, are normal because of maturing foundation and deficient upkeep.
- Water and sterilization foundation, especially in metropolitan regions, faces difficulties.
- The government has focused on foundation improvement for monetary development and venture.
- Public transportation incorporates transports and worker minibusses (known as “kombis”).
- Improvements in foundation, particularly energy and water, are basic for financial turn of events and personal satisfaction.
Facts about Zimbabwe Natural Resources
- Zimbabwe is wealthy in normal assets, including gold, platinum, precious stones, coal, and agrarian land.
- Gold is a significant product, with enormous scope mining tasks and distinctive diggers.
- Platinum stores in the Incomparable Dyke locale are among the biggest on the planet.
- Diamonds, especially from the Marange fields, stand out.
- Agriculture is a critical area, with rich soils supporting yields like maize, tobacco, and cotton.
- The nation has different untamed life, adding to the travel industry.
- Forests in Zimbabwe give lumber and other timberland items.
- Challenges incorporate unlawful mining, ecological corruption, and unreasonable land use rehearses.
- The government has tried to draw in interest in mining and horticulture.
- Sustainable administration of regular assets is pivotal for long haul monetary and ecological manageability.
Facts about Zimbabwe Tourism
- Zimbabwe offers different the travel industry attractions, including normal marvels and social legacy.
- Victoria Falls, perhaps of the biggest cascade on the planet, is a significant draw for vacationers.
- Hwange Public Park is prestigious for its untamed life, including elephants, lions, and giraffes.
- Mana Pools Public Park offers open doors for safari and outside undertakings.
- The Extraordinary Zimbabwe ruins, an UNESCO World Legacy Site, feature old stone design.
- Matobo Public Park is known for its stone arrangements and old San rock craftsmanship.
- Lake Kariba offers fishing, drifting, and houseboat get-aways.
- Adventure exercises, for example, wilderness boating on the Zambezi Stream are famous.
- Cultural the travel industry incorporates visits to conventional towns, make markets, and social exhibitions.
- The the travel industry has potential for development, requiring interest in framework and advancement.
Facts about Zimbabwe Future Prospects
- Zimbabwe’s future possibilities rely upon different variables, including political soundness and financial changes.
- Economic enhancement past mining and farming is viewed as fundamental for manageable development.
- Investment in framework, especially energy and transportation, is significant.
- Improving the business climate to draw in unfamiliar venture is vital.
- Land change arrangements and farming efficiency will affect food security and monetary solidness.
- Education and abilities improvement are key for a serious labor force.
- Climate change variation and supportable regular asset the executives are difficulties for what’s to come.
- Strengthening majority rule foundations and maintaining basic freedoms will add to solidness.
- Promoting the travel industry and social businesses can help financial development and make occupations.
- International organizations and territorial collaboration will assume parts in Zimbabwe’s advancement way.
Conclusion
Zimbabwe is currently facing political changes, economic challenges, and social development while preserving its rich cultural heritage. The country’s diverse landscapes and historical sites attract tourists and reflect its complex history. Zimbabwe’s focus on international relations, education, and infrastructure promises a hopeful future. By addressing governance issues and promoting inclusivity and sustainable development, Zimbabwe aims to create a brighter future for its people and make positive contributions globally. It is a nation with a proud history and potential for prosperity, driven by unity and progress.
For more Information Content must visit Facts Real
Frequently Asked Questions & Answers
What is the authentic setting of Zimbabwe?
Zimbabwe has a staggering history, from old municipal foundations like the Unique Zimbabwe Domain to colonization by the English in the late nineteenth hundred years. It obtained independence from English rule in 1980, with Robert Mugabe as its most essential top of the state.
What vernaculars are spoken in Zimbabwe?
Zimbabwe sees 16 power lingos, with English, Shona, and Ndebele being the most by and large spoken. Various lingos integrate Chewa, Kalanga, Sotho, Tonga, and Venda.
How can what is occur in Zimbabwe?
Zimbabwe works under a semi-official system, with Emmerson Mnangagwa as the continuous president. The choice party, ZANU-PF, has been in power since independence. Political security, fundamental opportunities, and financial changes are advancing troubles.
What is the economy of Zimbabwe considering?
Zimbabwe’s economy relies upon cultivating (maize, tobacco, cotton), mining (gold, platinum, gems), and the movement business. It has stood up to challenges like crazy expansion and joblessness.
What are a few renowned social parts of Zimbabwe?
Zimbabwean culture is rich with customary music (mbira), dance (Gwara), stone figures, and dynamic texture (Chitenge/Shweshwe). The Incomparable Zimbabwe remains and Shona model are notable social images.
How assorted is Zimbabwe’s general public?
Zimbabwe’s general public is different, with the Shona and Ndebele as the biggest ethnic gatherings. Family and local area are focal, and there’s a blend of metropolitan and country ways of life. The nation has a moderately youthful populace.
What are the significant normal attractions in Zimbabwe?
Zimbabwe is known for Victoria Falls, Hwange Public Park (untamed life), Mana Pools (safari), Matobo Slopes (rock developments), and Lake Kariba (fishing, drifting). These attractions draw vacationers from around the world.
How has Zimbabwe tended to ladies’ freedoms?
While Zimbabwe ensures orientation uniformity in its constitution, ladies actually face difficulties like underrepresentation in governmental issues and orientation based savagery. Endeavors are continuous to advance strengthening and uniformity.
What are a few difficulties confronting Zimbabwe?
Zimbabwe faces difficulties, for example, joblessness, neediness, political shakiness, medical care access, and environmental change influences. Financial changes, foundation advancement, and social projects are key areas of concentration.
What is the future standpoint for Zimbabwe?
The fate of Zimbabwe relies upon factors like political security, financial broadening, framework improvement, and worldwide relations. With versatility and purposeful endeavors, Zimbabwe holds back nothing and advancement.
For more Information about Zimbabwe visit Wikipedia.org
