- Introduction to Japan:
- Facts about Japan History:
- Facts about japan Culture:
- Facts about Japan Geography:
- Facts about Japan Political Situation:
- Facts about Japan Economy:
- Facts about Japan Society:
- Facts about Japan Ethnic Diversity:
- Facts about Japan Languages:
- Facts about Japan Religion:
- Facts about Japan Conflict and War:
- Facts about Japan Reconstruction Efforts:
- Facts about Japan International Relations:
- Facts about Japan Humanitarian Issues:
- Facts about Japan Women’s Rights:
- Facts about Japan Education:
- Facts about Japan Infrastructure:
- Japan Currency
- Facts about Japan Natural Resources:
- Facts about Japan Tourism:
- Facts about Japan Future Prospects:
- Conclusion:
- Japan Map
- Frequently Asked Questions about Japan:
Introduction to Japan:
Settled in the western Pacific Sea, Facts about Japan is a dazzling archipelago that flawlessly mixes old customs with state of the art innovation. Its rich history traverses centuries, from the unbelievable starting points of its most memorable sovereign to the cutting edge period of monetary ability and social impact. Japan’s lively culture, beautiful scenes, and clamoring urban areas have spellbound the minds of explorers and researchers the same. From the tranquil sanctuaries of Kyoto to the neon-lit roads of Tokyo, Japan offers an embroidery of encounters for those looking for a brief look into its interesting legacy and dynamic present.
Facts about Japan History:
- Japan’s written history goes back north of 2,000 years, with its previously known sovereign, Jimmu, climbing to the privileged position in 660 BCE as per legend.
- The primitive period of Japan, especially the Tokugawa Shogunate from 1603 to 1868, saw the nation segregated from the remainder of the world until the Meiji Reclamation.
- The Meiji Reclamation in 1868 denoted Japan’s modernization, with quick industrialization and westernization.
- Japan arose as a frontier power in the mid twentieth 100 years, attaching Taiwan, Korea, and portions of China.
- World Conflict II saw Japan’s loss in 1945, prompting the U.S. occupation and ensuing financial resurgence.
- Japan’s post-war constitution denies battle as a sovereign right and underlines pacifism.
- The Unified control of Japan under Broad Douglas MacArthur managed critical changes in legislative issues, society, and training.
- Japan’s “monetary wonder” in the late twentieth century pushed it to turn into the world’s second-biggest economy.
- Japan’s set of experiences incorporates a rich practice of expressions like Kabuki theater, tea functions, and conventional music like gagaku.
- Modern Japan has a profound worship for its verifiable locales, including old sanctuaries, palaces, and holy places.
Facts about japan Culture:
- Japanese culture is famous for its accentuation on agreement, regard, and scrupulousness.
- Traditional Japanese expressions like Ikebana (bloom orchestrating) and Origami (paper collapsing) are polished around the world.
- Manga and anime are well known social products, affecting worldwide diversion.
- The idea of “wa” (concordance) is profoundly implanted in Japanese culture, impacting social cooperations and navigation.
- Sumo wrestling is a conventional game that holds strict and social importance.
- Cherry bloom celebrations (Hanami) in spring and vivid fall foliage seeing (Momijigari) are valued occasional customs.
- Tea functions, where matcha (powdered green tea) is ready and served, are emblematic of Japanese cordiality and Harmony standards.
- Traditional clothing like the kimono and yukata are as yet worn for extraordinary events.
- Karaoke, a Japanese creation, has turned into a worldwide peculiarity.
- Japanese food, including sushi, ramen, and tempura, is praised overall for its flavor and show.

Facts about Japan Geography:
- Japan is an archipelago comprising of north of 6,800 islands, with four primary islands: Honshu, Hokkaido, Kyushu, and Shikoku.
- The nation is situated in the Pacific Sea, east of the Korean Landmass.
- Japan is known for its assorted topography, including mountains, backwoods, and fields.
- Mount Fuji, a notable image of Japan, is the country’s most elevated top at 3,776 meters (12,389 feet).
- The “Ring of Fire” around Japan brings about incessant tremors and volcanic movement.
- Due to its hilly territory, Japan has restricted arable land, prompting imaginative farming practices like terraced rice paddies.
- Japan’s environment shifts from subtropical in the south to calm in the north, with unmistakable four seasons.
- The nation has a rich biodiversity, with extraordinary vegetation like the Japanese macaque (snow monkey) and cherry blooms.
- Japan’s shore is broad, giving chances to fishing and oceanic businesses.
- The Seto Inland Ocean, a waterway between Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu, is dabbed with beautiful islands and islets.
Facts about Japan Political Situation:
- Japan is a parliamentary majority rules government with an established government.
- The Sovereign of Japan is an emblematic nonentity, with the State head holding leader power.
- The Public Eating regimen is Japan’s bicameral lawmaking body, comprising of the Place of Delegates and the Place of Councilors.
- The Liberal Progressive faction (LDP) has been a prevailing political power beginning around 1955, with brief times of resistance rule.
- Japan’s political framework accentuates agreement building and solidness.
- Prime Priest Yoshihide Suga succeeded Shinzo Abe in 2020, proceeding with the LDP’s authority.
- Japan’s political scene incorporates different gatherings, for example, the Protected Leftist alliance and the Komeito Party.
- Issues like a maturing populace, monetary changes, and social government assistance are fundamental to political talk.
- Local administration in Japan is separated into prefectures, urban areas, towns, and towns.
- The Japanese Self-Preservation Powers (JSDF) are unavoidably ordered for self-protection purposes and helpful missions.
Facts about Japan Economy:
- Japan has an exceptionally evolved and mechanically progressed economy, known for developments in car, gadgets, and mechanical technology ventures.
- The Japanese yen (JPY) is the authority money, and Tokyo is a worldwide monetary center.
- Companies like Toyota, Sony, and Nintendo are globally perceived Japanese brands.
- Japan has serious areas of strength for a situated economy, especially in vehicles, hardware, and gadgets.
- The “Lost Ten years” of the 1990s and mid 2000s saw Japan’s financial development delayed after a property market slump.
- The government carried out financial improvement measures to battle collapse and advance development.
- Japan is an individual from the G20 and has international alliances with different nations.
- The maturing populace and low rate of birth present difficulties to Japan’s economy and social government assistance framework.
- Agriculture, albeit a little level of Gross domestic product, is profoundly proficient, with rice being a staple yield.
- Tourism is a critical supporter of the economy, with a large number of guests attracted to Japan’s way of life, history, and regular magnificence.
Facts about Japan Society:
- Japanese society puts serious areas of strength for an on regard, pecking order, and social concordance.
- Group mindset is predominant, with faithfulness to family, organization, or local area profoundly esteemed.
- “Salarymen,” or middle class laborers, frequently have long work hours and worker dedication.
- Japan has one of the world’s most noteworthy futures, credited to a sound eating routine and all inclusive medical services.
- The idea of “hiding any hint of failure” (keeping up with nobility and staying away from humiliation) is vital to social connections.
- Traditional orientation jobs endure, however there are continuous endeavors to advance orientation uniformity.
- Aging populace and declining rates of birth are huge segment difficulties.
- Education is exceptionally esteemed, with a thorough framework stressing tests and accomplishment.
- Japan has a low crime percentage and solid local area policing.
- The idea of “omotenashi,” or benevolent cordiality, is profoundly imbued in Japanese culture.
Facts about Japan Ethnic Diversity:
- Japan is transcendently ethnically homogeneous, with more than 98% of the populace being of Japanese plunge.
- The biggest minority bunch is the Ainu, a native group fundamentally from Hokkaido.
- Zainichi Koreans are one more huge minority, relatives of Koreans who came to Japan during the frontier time frame.
- There are more modest networks of Chinese, Filipinos, Brazilians, and different identities.
- Despite the homogeneity, Japan is progressively turning out to be more assorted because of worldwide relocation and globalization.
- Issues of segregation and combination influence some minority networks.
- Efforts are being made to perceive and save the way of life and freedoms of native Ainu individuals.
- Schools and public organizations are attempting to advance multicultural comprehension and inclusivity.
Facts about Japan Languages:
- The authority and most broadly communicated in language in Japan is Japanese, which has a few lingos across various districts.
- The Japanese composing framework incorporates kanji (characters acquired from Chinese), hiragana, and katakana (syllabic contents).
- English is educated as a subsequent language in schools, and many signs in significant urban communities are bilingual.
- Ainu, a jeopardized language spoken by the Ainu public, is perceived as a social resource.
- Ryukyuan dialects are spoken in the Ryukyu Islands, with Okinawan being the most noticeable.
- Due to Japan’s set of experiences of disengagement, loanwords from different dialects, especially English, are normal in present day Japanese.
- Japanese Gesture based communication (JSL) is utilized by the hard of hearing local area and contrasts fundamentally from American Gesture based communication (ASL).
- Japanese is a language with complex honorifics, reflecting economic wellbeing and connections.
- The utilization of keigo (courteous language) is significant in conventional settings, like business and official correspondences.
- With globalization, the more youthful age is more presented to and capable in worldwide dialects like English, particularly in metropolitan regions.
Facts about Japan Religion:
- Shintoism is Japan’s native religion, underlining kami (spirits) in nature, predecessors, and customs at sanctums.
- Buddhism, acquainted with Japan from China and Korea, exists together with Shintoism and has numerous disciples.
- Shinto customs are in many cases seen during significant life altering situations like weddings and births.
- Buddhist practices, for example, reflection and sanctuary visits, are normal for functions and thought.
- Many Japanese individuals practice a syncretic mix of Shinto and Buddhist convictions.
- Christianity is a minority religion in Japan, with under 1% of the populace distinguishing as Christian.
- Religious resistance is by and large high in Japan, with a common way to deal with administration.
- New strict developments, known as “Shinshukyo,” have arisen in present day Japan, offering elective otherworldly ways.
- Festivals like Obon (respecting progenitors’ spirits) and Shichi-Go-San (praising youngsters’ development) are strict in beginning.
- Traditional expressions like Noh theater frequently integrate strict topics and stories from Shinto and Buddhist customs.
Facts about Japan Conflict and War:
- Japan’s contribution in The Second Great War started with its attack of Manchuria in 1931, trailed by clashes with China.
- The assault on Pearl Harbor in 1941 brought Japan into The Second Great War against the Unified Powers.
- The Pacific Conflict saw wild fights, including the Skirmish of Halfway and the island-jumping efforts.
- The conflict finished in Japan’s acquiescence in 1945 after the nuclear bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki.
- Post-war Japan was under Associated occupation, drove by the US, which brought huge changes.
- Japan’s military, the Japan Self-Protection Powers, is intrinsically restricted to self-preservation and philanthropic missions.
- Controversies encompass Japan’s wartime history, including issues of solace ladies and atrocities.
- Japan has a conservative constitution, Article 9, which disavows the option to take up arms or keep a military.
- Yasukuni Sanctum in Tokyo is a disputed matter because of its reverence of war dead, including war hoodlums.
- Efforts to recollect the conflict incorporate exhibition halls like the Hiroshima Harmony Remembrance and the Yasukuni War Historical center.
Facts about Japan Reconstruction Efforts:
- After The Second Great War, Japan went through broad reproduction, known as the “post-war financial wonder.”
- The Marshall Plan gave help to Japan’s reproduction, zeroing in on modern recuperation and framework.
- Japanese businesses, like gadgets and autos, were reconstructed with current innovations.
- The government executed land changes and put resources into training to spike monetary development.
- The 1964 Tokyo Olympics represented Japan’s fruitful recuperation and return to the global stage.
- The Tohoku quake and tidal wave in 2011 prompted huge recreation endeavors in the impacted regions.
- The Japanese government allotted billions of dollars for revamping foundation, homes, and organizations.
- Initiatives like the “Recreation Organization” were laid out to facilitate recuperation endeavors and backing networks.
- Challenges included radiation cleanup after the Fukushima atomic debacle and tending to dislodged populaces.
- Public-private organizations and global help assumed pivotal parts in the remaking system.
Facts about Japan International Relations:
- Japan is a critical partner of the US, facilitating U.S. army installations under the U.S.- Japan Security Arrangement.
- The “Three Non-Atomic Standards” of not creating, having, or permitting atomic weapons on Japanese region guide its international strategy.
- Japan has regional questions with China over the Senkaku/Diaoyu Islands and with South Korea over Dokdo/Takeshima.
- Economic binds with China are solid, albeit political strains exist because of verifiable and regional issues.
- Japan keeps up with close conciliatory relations with nations in the Asia-Pacific locale, including South Korea and ASEAN countries.
- Japan has been a functioning member in worldwide associations like the Assembled Countries and G7.
- Cultural strategy, including the advancement of Japanese mainstream society (Cool Japan), has been a focal point of international strategy.
- Japan’s “Free and Open Indo-Pacific Methodology” expects to advance dependability and success in the district.
- Humanitarian guide and calamity aid projects have improved Japan’s worldwide standing.
- Trade arrangements, like the Exhaustive and Moderate Understanding for Transoceanic Organization (CPTPP), exhibit Japan’s obligation to worldwide monetary combination.
Facts about Japan Humanitarian Issues:
- Japan countenances difficulties with its maturing populace and declining rate of birth, prompting worries about a contracting labor force.
- Homelessness is a social issue, with evaluations of many thousands living in the city or in brief sanctuaries.
- The 2011 Fukushima atomic fiasco brought about uprooting and progressing worries about radiation openness.
- Mental medical problems, like sadness and self destruction, are huge, particularly among the young and older.
- Discrimination against minority gatherings, including the Ainu and Zainichi Koreans, perseveres.
- Japan has a high self destruction rate, with factors including cultural strain, financial difficulty, and psychological wellness shame.
- The maturing populace presents difficulties for medical services and senior consideration frameworks.
- Natural fiascos, for example, seismic tremors and tropical storms, present repeating compassionate difficulties.
- Child destitution rates have been a worry, with endeavors to address this through friendly government assistance programs.
- Efforts to advance inclusivity and backing weak populaces are progressing, remembering against harassing lobbies for schools.
Facts about Japan Women’s Rights:
- Despite advancement, Japan faces difficulties in accomplishing orientation correspondence in the work environment and society.
- The orientation pay hole stays huge, with ladies procuring on normal 23% not as much as men.
- Japan positions low in worldwide orientation correspondence files, for example, the World Monetary Gathering’s Orientation Hole Record.
- Traditional orientation jobs frequently put demands on ladies to focus on family over vocation.
- The term “Matahara” (maternity provocation) alludes to victimization pregnant ladies and moms in the work environment.
- Initiatives, for example, “Womenomics” expect to increment female support in the labor force and positions of authority.
- Japan has a low level of ladies in corporate meeting rooms and political positions.
- Childcare help and parental leave approaches have improved, however challenges stay in adjusting work.
Facts about Japan Education:
- Japan has a profoundly respected school system, with necessary training for kids matured 6 to 15.
- The framework incorporates primary school (first to sixth grade), middle school (seventh to ninth grade), and secondary school (tenth to twelfth grade).
- High school placement tests are urgent, deciding admission to esteemed schools and colleges.
- Japan’s scholastic year begins in April, with three semesters: April to July, September to December, and January to Spring.
- The nation has a high proficiency rate, with a solid accentuation on math and science training.
- The college placement test, the “Public Center Test for College Affirmations,” is taken by most understudies.
- Japan is home to all around the world eminent colleges like the College of Tokyo and Kyoto College.
- Extracurricular exercises, known as “bukatsu,” are a fundamental piece of training, advancing collaboration and discipline.
- Vocational schooling, known as “kosen,” gives particular preparation in fields like designing and innovation.
- Education change conversations center around encouraging inventiveness, decisive reasoning, and worldwide viewpoints.
Facts about Japan Infrastructure:
- Japan flaunts progressed foundation, including proficient public transportation like Shinkansen (projectile trains) and broad tram organizations.
- Tokyo’s Narita and Haneda air terminals are significant worldwide centers, with proficient rail associations with urban communities.
- The nation has a thick organization of interstates and streets, with very much kept up with turnpikes.
- Japan is known for its tremor safe structures and foundation because of its regular seismic movement.
- The Tokyo Skytree, one of the world’s tallest pinnacles, represents Japan’s cutting edge design and designing.
- Advanced innovation is coordinated into foundation, including savvy parkways and automated stopping frameworks.
- Japan has put resources into environmentally friendly power, with sun based power and wind ranches adding to its energy blend.
- Public offices like parks, libraries, and public venues are very much planned and open.
- The Tokyo 2020 Olympic Games prodded foundation enhancements, including new arenas and transportation overhauls.
- High-speed web and inescapable Wi-Fi inclusion are normal all through the country.
Japan Currency

Facts about Japan Natural Resources:
- Japan is generally poor in normal assets, prompting weighty reliance on imports.
- Forests cover around 66% of the nation, giving lumber and supporting biodiversity.
- Limited arable land has prompted effective horticultural practices, with rice as a staple harvest.
- Japan has little saves of minerals like coal, copper, and iron metal, requiring imports for modern creation.
- Fisheries are a huge normal asset, with Japan being one of the world’s biggest fishing countries.
- Water assets are painstakingly made due, with productive water system frameworks for agribusiness.
- Geothermal energy is used because of Japan’s volcanic action, with geothermal power plants in activity.
- Renewable energy sources like sunlight based and wind power are progressively significant for Japan’s energy security.
- Japan’s rugged landscape gives potential open doors to hydropower age.
- Conservation endeavors are set up to safeguard Japan’s normal assets and biodiversity.
Facts about Japan Tourism:
- Japan is a famous vacationer location known for its rich culture, verifiable locales, and regular excellence.
- Tokyo, the capital, offers a blend of current high rises, noteworthy sanctuaries, and dynamic areas.
- Kyoto is well known for its customary sanctuaries, cultivates, and saved geisha regions.
- Osaka draws in guests with its vivacious food scene, shopping locale, and General Studios Japan.
- Hokkaido, Japan’s northern island, is known for its ski resorts, underground aquifers, and grand scenes.
- Hiroshima’s Tranquility Commemoration Park and Miyajima Island’s notorious drifting torii door are huge authentic locales.
- Cherry bloom season (sakura) in spring and harvest time foliage (koyo) in fall draw in large number of guests.
- Traditional ryokan (motels) and onsen (natural aquifers) offer exceptional social encounters.
- Japan’s culinary scene, including sushi, ramen, and kaiseki, is a significant draw for food fans.
- Cultural occasions like sumo competitions, tea functions, and celebrations (matsuri) give vivid encounters to travelers.
Facts about Japan Future Prospects:
- Japan faces difficulties, for example, a maturing populace and declining rate of birth, affecting labor force and social government assistance frameworks.
- Innovations in mechanical technology and man-made brainpower are areas of development, with Japan driving in innovative work.
- The government plans to rejuvenate rustic regions and advance supportable agribusiness.
- Renewable energy improvement, including seaward wind ranches and hydrogen power, is a concentration for energy security.
- Japan’s medical care area is supposed to develop to address the issues of a maturing populace.
- International coordinated efforts in science and innovation are probably going to keep, encouraging advancement.
- Efforts to advance the travel industry, particularly in less popular districts, are supposed to help neighborhood economies.
- Urban advancement projects intend to make brilliant urban communities with productive transportation and green spaces.
- The shift towards a computerized economy and web based business is probably going to speed up.
- Continued accentuation on training change to sustain imagination, worldwide viewpoints, and decisive reasoning abilities for people in the future.
Conclusion:
All in all, Japan remains as an enamoring mix of custom and development, offering a brief look into an existence where old traditions orchestrate with present day progressions. Its unpredictable history, well established in Shintoism and Buddhism, has molded a general public known for its veneration for nature and steady strength. As Japan explores the difficulties of a maturing populace, monetary movements, and worldwide availability, its future possibilities stay promising.
Japan Map
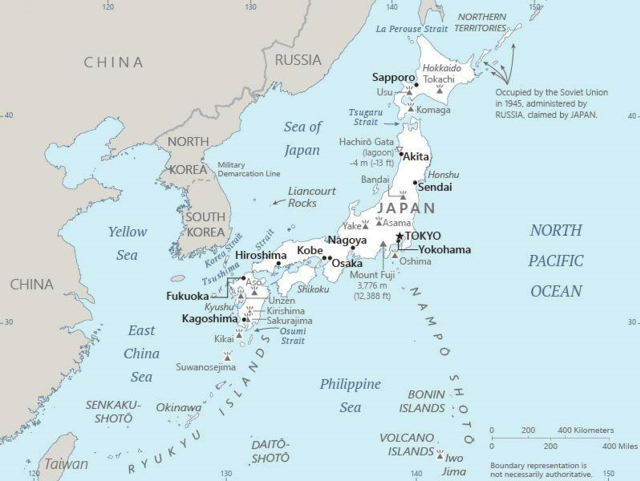
also read 25+ Best facts about Indonesia
Frequently Asked Questions about Japan:
What is the capital of Japan?
The capital of Japan is Tokyo, one of the world’s most crowded and lively urban communities.
What is the cash utilized in Japan?
The authority cash of Japan is the Japanese Yen, indicated by the image ¥ and the code JPY.
When is the best chance to visit Japan?
The best opportunity to visit Japan relies upon individual inclinations. Spring (Walk to May) is popular for cherry blooms, while harvest time (September to November) offers staggering fall foliage. Winter (December to February) is great for winter sports, and summer (June to August) brings lively celebrations.
What are some must-attempt Japanese dishes?
Some must-attempt Japanese dishes incorporate sushi (crude fish on prepared rice), ramen (noodle soup), tempura (battered and broiled fish or vegetables), and okonomiyaki (exquisite flapjack).
Is it challenging to go around Japan without communicating in Japanese?
While some fundamental information on Japanese can be useful, Japan has amazing public transportation with signs in English. Numerous vacationer regions have English-talking staff, and interpretation applications can be valuable.
What are some well known vacation destinations in Japan?
Well known attractions in Japan incorporate the noteworthy sanctuaries of Kyoto, the clamoring roads of Tokyo’s Shibuya and Shinjuku locale, the famous Mount Fuji, the conventional roads of Kanazawa, and the Hiroshima Harmony Commemoration Park.
Are there any manners tips guests ought to be aware prior to going to Japan?
Indeed, it is essential to notice nearby traditions. Bowing is a typical hello, shoes ought to be eliminated while entering homes and a few cafés, and it’s well mannered to say “Arigatou gozaimasu” (Thank you) and “Sumimasen” (Excuse me/sorry).
What is the customary Japanese apparel?
The conventional Japanese dress incorporates the kimono, a proper robe worn for exceptional events, and the yukata, a lighter cotton robe frequently worn during summer celebrations or at underground aquifers.
Is it protected to drink tap water in Japan?
Indeed, faucet water in Japan is for the most part protected to drink. It is of excellent and satisfies severe wellbeing guidelines. Nonetheless, certain individuals might favor filtered water because of individual inclination.
What are a few remarkable social encounters to attempt in Japan?
A few remarkable social encounters in Japan incorporate partaking in a tea function (Chanoyu), taking a stab at a kimono and taking photographs, remaining at a customary ryokan (motel) with tatami mat floors and resting on futons, and seeing a sumo wrestling match or kabuki theater execution.
for more information about Japan visit Wikipedia.org
